Table Of Content

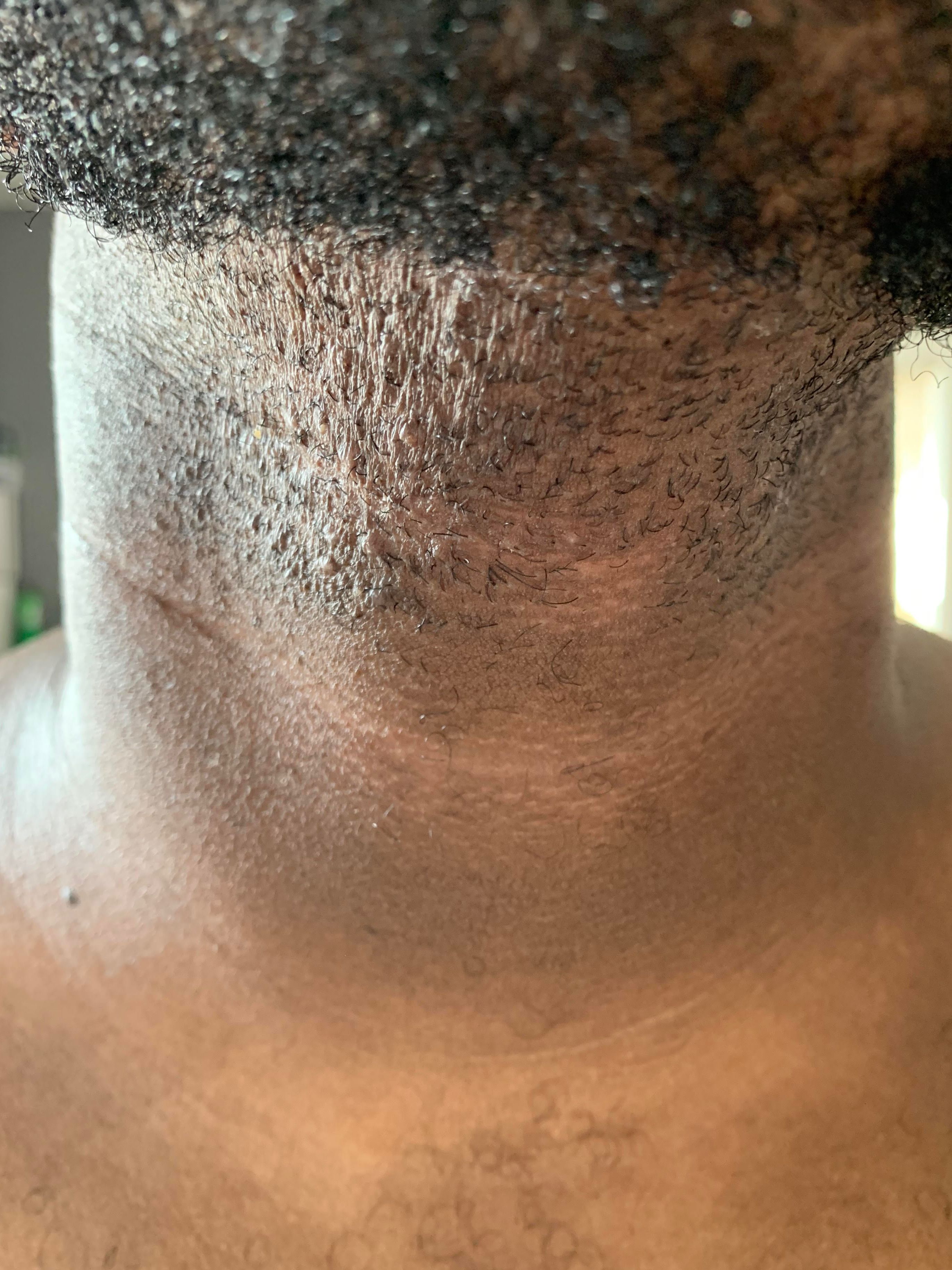
Try to avoid pulling or stretching the skin as well. If you want to continue shaving, you should consider using a razor with a skin guard. Or, you can swap out razors entirely and use electric clippers or hair removal creams instead. Because they tend to have tightly curled hair, people of African descent are more likely to have ingrown hair. The tight curls can more easily curl back into the skin and also can become sharper after shaving because of the curl's angle. If these at-home remedies aren’t working, step away from the tweezers and call your doctor.
How long do ingrown hairs last?
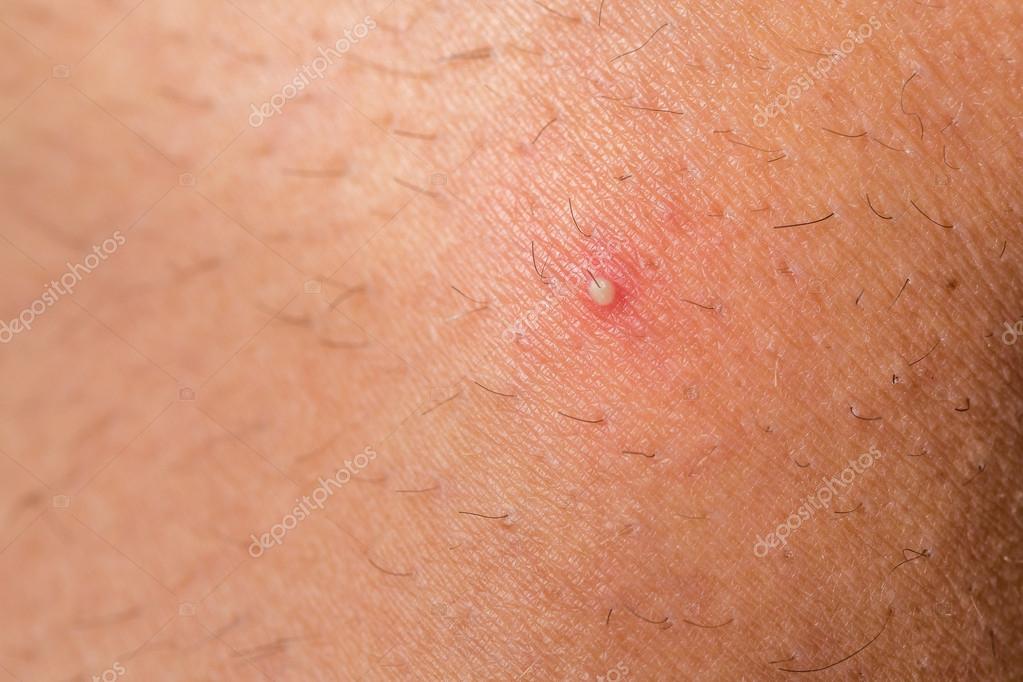
To prevent scarring or infection, don’t pick at, scratch or pop your ingrown hairs. Ingrown hairs are common in areas where people shave. They happen when the skin blocks the emergence of a hair from the follicle, or when a hair grows back into the skin. Preventing ingrown hairs can decrease your risk of related infections. Never pick or pop an infected ingrown hair, as this also increases the risk of complications.
Ingrown Hairs (Pseudofolliculitis)
For people with sensitive skin, creams may not be the best option since the products can be harsh on the skin if not used properly. Electric clippers may leave the hair longer than if you were to use a razor. If the hair is longer, it may be less likely to become embedded as an ingrown hair. Thankfully, there are steps you can take to manage ingrown hair—and prevent it from happening in the first place.
190 ingrown hair stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free for download.
If the site of the ingrown hair acquires an infection with Staphylococcus aureus, it can cause itchy bumps, pain, flushed skin, and pus. Epilation zones set of line icons in vector, editable stroke. Illustration legs shins and thighs, hands and bikini area, face lip area and armpits, tendency to ingrown hairs.
Raised Skin Bumps: Pictures, Symptoms, Causes, Treatments - Women's Health
Raised Skin Bumps: Pictures, Symptoms, Causes, Treatments.
Posted: Fri, 08 Sep 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
How can I prevent ingrown hair?
Treatments for an infected ingrown hair vary based on the type and severity of the infection. Your healthcare provider can help you decide how to address your ingrown hair directly. You can also try other hair removal methods that are less likely to lead to ingrown hairs. Those include creams that dissolve hair and a laser or electric current (electrolysis) to remove the hair follicle for good.
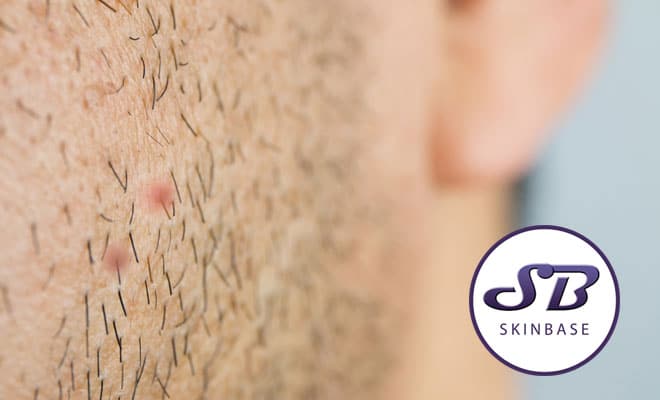

Antibiotics are necessary to treat staph infections. However, a person may find temporary symptom relief by taking over-the-counter painkillers or holding a clean, cold compress over the wound. If the staph infection is resistant to antibiotics, a doctor can discuss appropriate alternative treatments with a person.
How do you remove an ingrown hair?
When new hair forms, if the hair follicle is closed up, hair can't grow out of the follicle and through the skin. Closeup of caucasian skin with ingrown hair and man short beard. Close up of caucasian skin with many ingrown hairs. The core goal of treatment for any of these cysts is to reduce their occurrence by keeping your skin exfoliated and moisturized. Body washes and lotions made with gentle glycolic acid will help.
If you continue having infected ingrown hairs in the same area, such as your face, you might consider other methods of hair removal, such as laser treatment. Many types of bacteria can cause infections in an ingrown follicle. While not all ingrown hairs will contract an infection with staph, some can develop this type of infection from a bacterium that usually lives on the skin. Possible treatments for razor bumps include keeping your skin moisturized and discontinuing shaving, which allows your ingrown hairs to grow out. It is also possible to develop a bacterial infection, especially if you are scratching at the ingrown hair.
Some prescription medications can help prevent ingrown hairs. Retinoid creams are effective in removing dead skin cells that may contribute to ingrown hairs. They can also help reduce scars from former infections. To reduce the chances of getting ingrown hair cysts, keep your skin clean and gently exfoliated and moisturized. If you do shave, don't shave too close, and always shave in the direction the hair grows.
Pores are the small holes in our skin that allow sweat and oil to reach the surface of the glands underneath. Topical and oral antibiotics may be required for severe cases that form pustules and abscesses, which indicate secondary infection. Hair removal creams dissolve the hair and will leave the ends of the hair softer, rather than sharp. But you should wait to use the creams until your skin has fully healed, as it can cause additional irritation.
Consulting a medical doctor who specializes in dermatology may be necessary for the optimal treatment of more severe cases. Although an ingrown hair can heal on its own and spontaneously dislodge, in some cases, it may be tough to get rid of it. Extrafollicular penetration can occur because shaving produces short hairs that are sharp enough to enter the skin. Transfollicular penetration can occur if you stretch your skin while shaving. You can’t always prevent ingrown hairs, but you can take steps to lower the chances of them developing. Exfoliation should be approached carefully, as it causes inflammation, which leads to hyperpigmentation and may not be very helpful in resolving ingrown hairs.